Understanding
THC
THC – Tetrahydrocannabinol
Biochemistry – What is Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) ?
Scientific research on THC began much earlier than most suspect. In 1964, well over 40 years ago, THC was studied first in Israel and has since spread to numerous countries across the globe. Dr Raphael Mechoulam first isolated and synthesised THC from the cannabis plant. Apparently, in his rush to conduct his research, Dr Mechoulam broke the law by acquiring cannabis from his friends at the police station. His research and isolation of THC back in 1964, marked the start of a long career dedicated to cannabis research. The discovery of THC paved the way for later discoveries earning Dr Mechoulam numerous honours. One recognition in particular he received was the NIDA Discovery Award in 2011.
THC is still illegal in many countries around the world, despite what medical research has provided evidence of its therapeutic properties. Strangely enough synthetic versions of the chemical have been legally prescribed for decades.
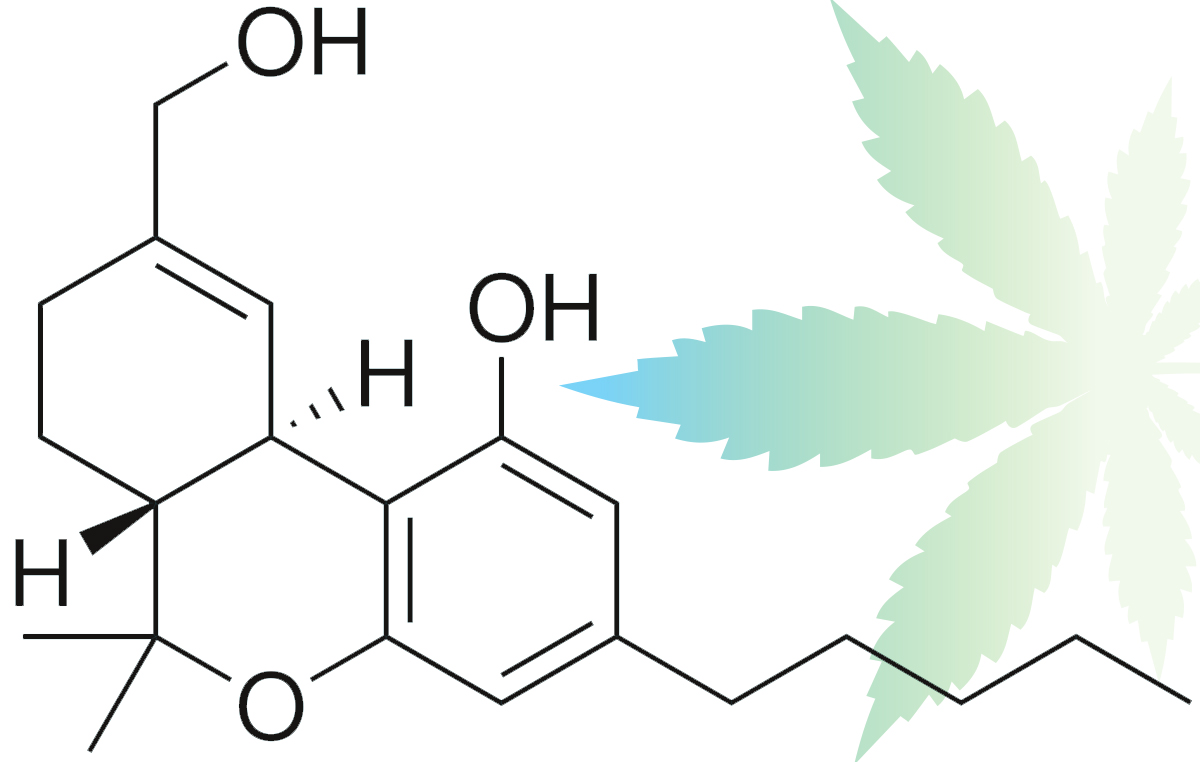
Medical Benefits of THC / Effects of THC
The first THC-based pharmaceutical, a pill sold as Marinol (scientific name: dronabinol), was created by a company called Unimed Pharmaceuticals. The source of funding for this project was none other than the National Cancer Institute. In 1985, Marinol received FDA approval to be prescribed as a treatment for chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting.
Since then, a number of other pharmaceuticals containing THC have been developed. Cesamet (nabilone), is one such medicine and is a synthetic isomer of THC. Sativex (nabiximols), administered as an oral spray is the whole cannabis extract.
- THC has been approved as a treatment for chemotherapy-related symptoms of nausea and vomiting
- THC can protect brain cells and stimulate their growth. THC has been proven to have a number of positive effects on brain cells. Most recreational drugs have been found to be neurotoxic. Strangely enough THC has an opposite effect and is considered a “neuroprotectant,” protecting brain cells from damage due to inflammation and oxidative stress. What’s more, scientists have even shown that THC has the ability to promote the growth of new brain cells. This is done through a process known as neurogenesis. This effect was first discovered in 2005 by researchers at the University of Saskatchewan.
Chemicals like THC are found naturally in the body
Following the discovery of THC, scientists searched for decades for similar chemicals in humans that could explain its effects and the mechanism of action.
In 1992, Dr. Mechoulam and his team made another breakthrough discovering a molecule called anandamide.
As it turns out, anandamide is one of a few cannabinoids produced in various parts of the human body and brain. Similar to the way opioids work by mimicking their natural counterparts, otherwise known as endorphins, the chemicals in cannabis mimic the naturally occurring cannabinoids within us called endocannabinoids.
(Endo – referring to Cannabinoids produced within the body naturally as opposed to within a plant)
Both anandamide and THC act on pathways in the body called cannabinoid receptors. In the brain, Most people know of THC due to its obvious ability to induce euphoria, or make one “high”. THC does not always have this effect on its own. The reason for this is that THC is mostly present in the cannabis plant as THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) which is its acidic precursor.
THCA is converted to THC when it is exposed to heat. This reaction is known as decarboxylation.
Sometimes, when plants are stored, small amounts of the acid may be converted to THC over time.
THC or Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol is psychoactive and responsible for many of the effects experienced by the cannabis user.
- Pain relief, the ability to relax, appetite stimulation
- THC has been shown to have anti-depressant effects
- THC has been shown to have anti-depressant effectsRecent research that suggests patients with a pre-disposition to schizophrenia as well as anxiety disorders should avoid steer clear of high-THC cannabis