Treatment Objectives
Anxiety and Depression Treatment
Anxiety and Depression Treatment
Typically anxiety and depression treatment involves the patient’s doctor prescribing an antidepressant medicine which should be coupled with psychotherapy and diet and lifestyle amendments. Patients are asked to commit to counselling on a regular basis, be vigilant with respect to taking their prescribed medication assuring that there are no interactions with anything else they may be taking. Being honest with medical practitioners about medication will eliminate any unnecessary contraindications. It is also suggested that patients stop or reduce any stimulants such as coffee, diet pills., particularly in cases where anxiety is debilitating.
Medication is typically prescribed for anxiety and depression treatment. Studies indicate that the SSRI’s and tricyclic antidepressants are very effective treatments for depression and anxiety. For extreme circumstances where the patient is experiencing panic and high levels of anxiety., benzodiazepines may also be prescribed for up to 3 weeks. This is typically how long it takes for most antidepressants to take effect. It is suggested that alongside medication, patients receive therapy to talk out their issues with a professional.
Medications for the Treatment of Anxiety and Depression
- SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor)
ie) citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline - SNRI (serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor)
ie) venlafaxine, duloxetine - Tricyclic antidepressant
ie) amitriptyline, imipramine, nortriptyline - Benzodiazepine
ie) alprazolam, clonazepam, diazepam, lorazepam - MAOI’s (monoamine oxidase inhibitors)
- Anticonvulsants
- Beta blockers
- Antipsychotics
Typical side effects of anxiety and depression medication
- Heart palpitations
- Sweating
- Tremor / Shakes
- Insomnia
- Sexual dysfunction
- Weight gain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headaches
- High blood pressure
Moreoften than not, when dealing with anxiety and depression, patient’s will undergo psychotherapy alongside taking an antidepressant medication. Psychological treatments help patient’s delve into the cause of their anxiety and depression. By talking through their issues with a professional, this can help open their awareness, change negative thought patterns and implement coping strategies moving forward. Psychological therapies have been shown highly effective in the treatment of anxiety and depression.
CBT(cognitive behaviour therapy) highlights the thought processes aligned with the patient’s behaviour, and has been found useful for people from all walks of life and age., young to the elderly .
Medical Cannabis Treatment of Anxiety
Anxiolytic
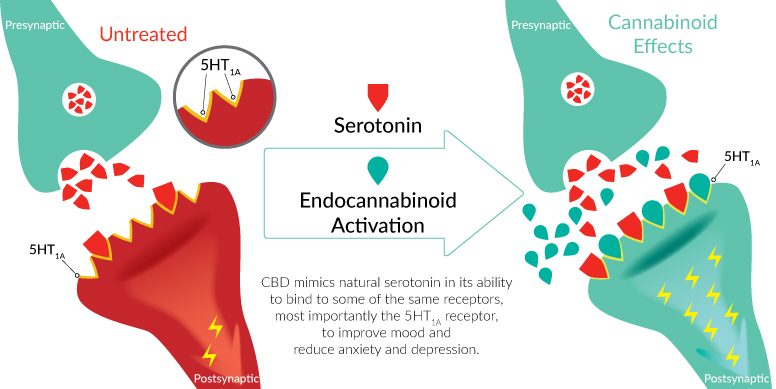
Serotonin is an essential neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of mood, sleep, appetite and libido. In the central nervous system serotonin communicates with numerous receptors responsible for a variety of biological functions.
The precise mechanism by which the endocannabinoid system modulates anxiety and depression is not fully understood. CBD is postulated to act as an agonist to the 5HT1areceptor. Activation of the 5HT1a receptor is understood to modulate the release of serotonin in the brain. This hypothesis was confirmed in a study in which mice were pretreated with a 5HT1a antagonist, the antidepressant effects of CBD were absent. Further evidence of the role of 5HT1a is given by the observed similarities of CBD and isapirone (a 5HT1a partial agonist) in public speaking model.
Neuroprotection
Impairment of the hippocampal neurogenesis has been associated with the pathogenesis of anxiety disorders and depression. CBD is though to stimulate hippocampal neurogenesis a property absent in CB1 knockout mice. The researchers postulate that the mechanism is hence CB1 dependent, CBD is thought to reduce the efficiency of FAAH hence reduce anandamide reuptake; hence the CB1 receptor is activated.
Brazilian Researchers Investigate CBD and how it may alleviate symptoms of Anxiety In Humans
Recruiting 10 patients with diagnosed Social Anxiety Disorder, the research team began by doing an analysis of patient brains via functional neuroimaging. Taking a look at the amount of bloodflow within various sections of the brain, the researchers were able to note how this changed upon CBD oil treatment.
In the first session, half of the patients received an oral dose of 400 mg of cannabidiol (CBD). The other half of the patients received placebos. Reversing these roles in the 2nd session, this gave all patients the opportunity of being treated with CBD. The results indicated CBD reduced anxiety in patients with social anxiety disorder and they pointed out how this was related to its effects on activity in limbic and paralimbic brain areas. According to the results of the study, cannabidiol (CBD) was associated with a significant decrease in subjective anxiety. Cerebral bloodflow after CBD treatment indicated an anxiolitic (anti-anxiety) effect in the areas of the brain that manage emotions.
Anxiety Statistics in Australia
One of the most common mental conditions in Australia, anxiety is prevalent. On average 1 in 3 women experience anxiety or will experience anxiety at some time in their life. For men, the statistic is 1 in 5. Therefore the national average for anxiety in Australia is 1 in 4 people.
Depression Statistics in Australia
It is said that on average, 1 in 6 people will experience depression in their lives. In women, the statistic is 1 in 5, and in men 1 in 8 men will experience depression. In Australia, it has been estimated that 45% of the population will suffer a mental health condition within their lifetime. Depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide and in any one year approximately 1 million Australian adults will have depression, whilst over 2 million will have anxiety. It is common for an individual to experience both anxiety and depression at the same time with one leading to the onset of the other.

What is Anxiety and Depression?
Anxiety and depression have varying degrees of severity, much like most illnesses., and it is a very personal experience. For some, their anxiety is disabling whereby the very thought of being in a room with strangers brings the body into full alert. The signals within the overly anxious person may be screaming RED ALERT, RED ALERT bringing on the sweats, raised blood pressure and and a heightened sense of awareness regarding their environment, people’s mannerisms, thoughts, and feelings and how they are of great threat to them. The proposed danger this person feels is extreme and hard to manage – particularly in places where it is deemed unnecessary. Some people who experience this kind of anxiety could be sitting in a business meeting, even amongst peers, and though they know they are safe – the body is responding with intense unrest.
Causes of Anxiety
One of the best ways to describe anxiety disorder is a fear or worry that gets so out of control it starts to affect and interfere with normal life. It is an extreme fear about almost anything concerning the past or future. Anxiety is causes by a combination of factors including:
- Changes in the brain
- Environmental stress
- Our family and upbringing
- Traumatic Event
Anxiety disorders start out in the brain. Scientists are considering the possibility that in some of those suffering from anxiety, there may be functional deficits in the brain circuitry that regulates fear and all the other emotions. Studies indicate that repeated exposure to stress has the propensity to alter nerve cells within the brain transmission that takes information from one part of the brain to another region for processing. It has been reported that those who suffer certain kinds of anxiety disorders have differences in the brain structure that control memories linked with strong emotions.
Symptoms of Anxiety
- Unrealistic fear or worry that causes a physical response
- Mental unrest
- Panic
- Can’t shut off from the day causing sleep difficulty
- Racing thoughts
- Racing heart
- Sweats
- Clammy and cold hands/feet
- Inability to be calm
- Dry Mouth
- Disorientation
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Quick tempered
- Feeling “crazy”
- Overthinking
- Overthinking
- Impatient
- On edge
- Chest Pain
- Headache
- Stomach Pain
- Blushing
Types of Anxiety Disorders
- Generalised Anxiety Disorder
- Social Anxiety
- Panic Attacks
- Panic Disorder
- Phobias
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Clinical Studies / References: