Understanding
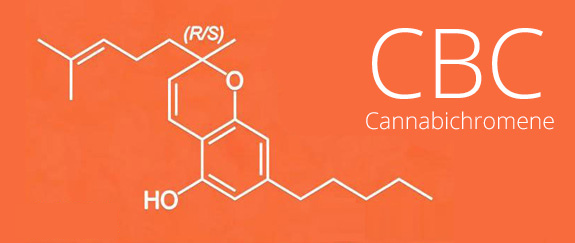
CBC
CBC – Cannabichromene
Biochemistry: What is Cannabichromene (CBC)
What is Cannabigerolic Acid (CBG-A)
With CBC-A, it travels by passing through the CBC synthase or through the enzymes responsible for getting the specific process underway.
In order to produce the cannabinoid known as cannabichromene (CBC), decarboxylation must occur.
What is decarboxylation?
It is rather interesting that in 2/3 of its chemical makeup, Cannabis is inactive until heated.
This is potentially why vapourising using ingestion delivers these raw plant acids most efficiently. Heating cannabis increases its potency. However, exposure to extreme temperatures for a prolonged period may destroy its active chemicals.
Over time, or quickly if exposed to heat, the CBC-A will lose a molecule of CO2; at this point, it is considered CBC. This same process applies when developing THC and CBD.
Medical Benefits of CBC / Effects of Cannabichromene
- Cannabichromene has anti-proliferative effects inhibiting the growth of cancerous tumours. Being on the brink of a cure for cancer, this finding is of great importance medically. It is proposed that the anti-prolifereative effects are a result of CBC’s interaction with Anandamide which is one of our bodies natural endocannabinoids. It effects both the CB1 and CB2 receptors and already has been found in studies to fight human breast cancer.
- Cannabichromene signs in minimizing inflammation. Inflammation is an immune reaction and plays a key role in many diseases.
- Cannabichromene has been found to reduce pain without the psychoactive effects.
- Cannabichromene has been identified to contribute to an overall mood elevation, helping relieve symptoms of depression.
- Cannibichromene believed to stimulate bone growth.
- Cannibichromene appears to increase the viability of developing brain cells. This brain growth (contrary to popular belief) continues in adulthood through a process called Neurogenesis. It only occurs in the hippocampus part of the human brain. The hippocampus is important for memory and learning. Lack of growth in this area contributes to a number of disorders including Alzheimers disease and depression. Previous studies regarding THC and CBD suggest they also promote neurogenesis. Alcohol and nicotine are known to inhibit brain growth, however CBC and other cannabinoids within the cannabis plant encourage and support brain growth.
- Cannibichromene successfully treats migraines.
Cannibichromene fights bacteria and fungi.