Treatment Objectives
Alzheimers Treatment
Alzheimers Treatment
Alzheimer’s disease is the leading cause of dementia and represents a progressive death of brain cells. Currently in order to slow down the degeneration, patients can obtain treatment in the form of 2 kinds of medications.
Medications for the treatment of Alzheimers
Cholinesterase Inhibitors – These medications are useful in preventing the breakdown of aetycholine which is a crucial messenger for memory. It also supports the communication in nerve cells. These are prescribed to delay worsening of symptoms and works for half those who take them.
- Donepezil (Aricept)
- Rivastigmine (Exelon)
- Galantamine (Razadyne)
Side effects may include nausea, loss of appetite, loosening of bowels and vomiting.
Memantine – Namenda is prescribed to Alzheimers patients who are suffering with moderate to severe symptoms. This medication regulates the activity of glutamate, which is a different neurotransmitter that assists in learning and memory.
Side effects may include headache, constipation, dizziness and possible confusion.
Medications for the treatment of behavioural symptoms in Alzheimer Patients
For a patient dealing with memory loss, Alzheimers disease may cause psychological and behavioural symptoms that require attention. This may include depression, anxiety, insomnia,agitation and aggressive behaviour. Medication may be required for relief in the way of anti-depressants, or tranquillisers (anti-psychotics).
Haloperidol (Serenace)
Typical side effects of Serenace
- stiffness (much like in Parkinson’s disease)
- shuffling gait
- shakiness
Risperidone (Risperdal) -appears to be helpful for the treatment of aggression and psychosis that occurs with Alzheimer’s disease
Typical side effects of Risperdal
- high risk for stroke
Medicinal cannabis & the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease:
Alzheimers Disease and Cannabis Treatment – Cannabinoids assist beta-amyloid plaque cross the blood-brain barrier
Researchers at the Roskamp Institute in Florida
Publisher: Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience Journal
New findings revealing how cannabinoids reduce one key indicator of Alzheimers disease. It has been known for some time that the loss of cell and brain tissue in the Alzheimer’s patient is linked up to a prevalence of beta-amyloid plaque. Levels of plaque in a patient’s brain also predicts just how severe the damage is within the patients brain tissue and reflects symptomatically.
The team of researchers and Corbin Bachmeier, Ph.D who led the study, explains that Alzheimer’s disease is not a result of abnormal production of the plaque. It is rather a result of impaired Aβ clearance. The study suggests that cannabis derived cannabinoids assist the plaque in crossing the blood-brain barrier. This is a process that is in full function for healthy people. Previous studies indicate that this process is blocked in Alzheimer’s patients.
Alzheimer’s Treatment Studied : 20mg/ kg CBD for 3 weeks
Australian Researchers study mice with Alzheimer’s Disease
Publisher: Psychopharmacology
Led by Dr. Tim Karl, another study originating out of Australia involved genetically engineered mice that had been treated with daily injections with 20 mg/kg of CBD for three weeks. The Australian research team investigated how chronic cannabidiol (CBD) treatment would affect the cognitive abilities of the mice studied. Comparing the results against mice that did not receive treatment, the findings were that CBD reversed the effects of cognitive impairment.
Single dose of cannabis derived CBD oil enough to reverse brain damage caused by high levels of iron in rats
Researchers from Brazil study was to show how CBD oil can protect the brain from degeneration and reverse impairments from high levels of iron.
Publisher: Molecular Neurobiology
High levels of iron promotes oxidative stress which causes brain degeneration and resulting memory loss. Published in Molecular Neurobiology researchers from Brazil were able to reverse the brain damage in rats by giving them a single dose of CBD oil.
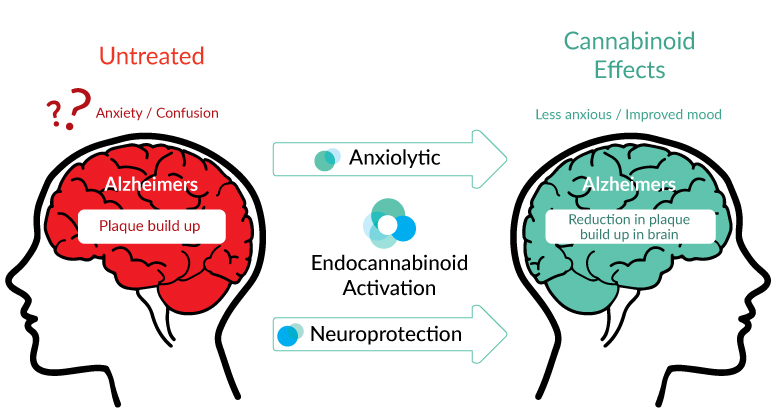

What is Alzheimers Disease?
- Alzheimers disease is a physical disease of the brain
- One of the leading causes of dementia
- Causes protein“tangles” that start to develop within the brain = death of brain cells
- Progressive disease that causes repetitive debilitating brain damage
- Results in complete deterioration of the patient mentally
Symptoms of Alzheimers Disease
- Loss of Memory – Confusion, Poor Name, Place and Event Recall
- Mood swings – Easy to scare, upset and anger, due to the increased memory loss and its impact within their life
- Withdrawal – Communication becomes a struggle due to the memory loss making emotional withdrawal very common
Causes of Alzheimers Disease
Scientists are aware that genes provide a strong predisposition to the development of Alzheimer’s. Genetic tests are available for both APOE-e4 and other rare genes that are a direct cause Alzheimer’s.
Risk genes increase the likelihood of developing a disease. Scientists have identified apolipoprotein E-e4 (APOE-e4) as a strong gene of risk. In 20-25% of Alzheimer’s cases, APOE-e4 may be a strong factor. Those who inherit APOE-e4 from both biological parents are at greater risk. Scientists have also discovered variations that directly cause Alzheimer’s disease in the genes coding three proteins: amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin-1 (PS-1) and presenilin-2 (PS-2).
Clinical Studies / References: