Treatment Objectives
Diabetes treatment
Diabetes treatment
Our bodies are systematic. There is a sophisticated process in every function. Our metabolism is a necessary process for our bodies – in order to live. In the case of Diabetes, our normal process of converting sugar from food into energy is disrupted. Essential to this conversion is Insulin. When insulin is no longer produced by a person or it is produced in inadequate amounts, this exchange doesn’t take place. Instead the sugar stays in the blood causing High Blood Glucose.
Diabetes treatment has one major goal across that board, and that is in the aim to keep blood glucose levels within a healthy target range. The key is balance. Balancing ones intake of food, with exercise and careful monitoring of prescribed medication.
Medication for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
- Sulfonylureas
- Biguanides
- Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
- Thiazolidinediones
- Meglitinides
- D-phenylalanine Derivatives
- DPP-IV Inhibitors
Blood Glucose Monitoring
To prevent the development of complications from diabetes, it is imperative that one maintain good blood glucose control. Checking your glucose levels regularly and as often as needed means it may be wise to get in the habit of doing self-blood glucose monitoring, so long as this has been approved by your doctor.
To self test blood glucose levels you will need the following:
A blood glucose meter
A lancet device with lancets
Test strips.
Usually when you are looking to purchase a blood glucose meter for diabetes treatment, you will find it sold as a kit with all the tools necessary to start up on your own. Most of these kits are available to purchase from Diabetes Australia but your doctor will often help you choose the best suited meter for your needs.
Alternative Therapies for Diabetes Treatment
Natural Supplements
Some diabetics have found Magnesium to be helpful in the improvement of blood sugar control. It has been studied that having a lack of magnesium has an association with insulin secretion abnormalities. This is turn is associated with diabetes complications.
Plant foods
- Brewer’s yeast
- Buckwheat
- Broccoli
- Peas
- Sage
Rich in fiber, most plant foods will be found beneficial for helping diabetics control their blood sugar levels.
Medical Cannabis Treatment for Diabetes
Many cannabinoids act just to inhibit prostaglandins and COX-2. Additionally they provide powerful anti-oxidant properties to salvage free radicals, and inhibit macrophage and TNF. Cannabis is an excellent anti-inflammatory that lacks the side effects of steroids (which diabetics have to avoid), the NSAIDS, and the COX-2 inhibitors like Vioxx. This anti-inflammatory action may help quell some of the arterial inflammation common in diabetes.
Cannabis is also neuroprotective. It is believed that much of neuropathy comes from the inflammation of nerves caused by glycoproteins in the blood that deposit in peripheral tissues and trigger an immune response. Cannabis helps protect the nerve covering (myelin sheath) from inflammatory attack. Cannabis also lessens the pain of neuropathy by activating receptors in the body and brain. Some components of cannabis (perhaps cannibidiol) act as anti-spasmodic agents similar to the far more toxic anti-convulsants like Neurontin. This action of cannabis helps relieve diabetic muscle cramps and GI upset.
Two other major actions of cannabis can benefit the diabetic. The first is helping to keep blood vessels open and improving circulation. Cannabis is a vasodilator and works well to improve blood flow. The second action is how cannabis can reduce blood pressure over time. While cannabis is not generally thought to be an anti-hypertensive and is no replacement for ACE inhibitors, it does contribute to lower blood pressure which is vital in diabetes management.
Night time can be particularly difficult for diabetics. A syndrome known as “restless leg syndrome” (RLS) is common. Cannabis helps still RLS which is otherwise treated with quinine and/or muscle relaxants like Flexaril.
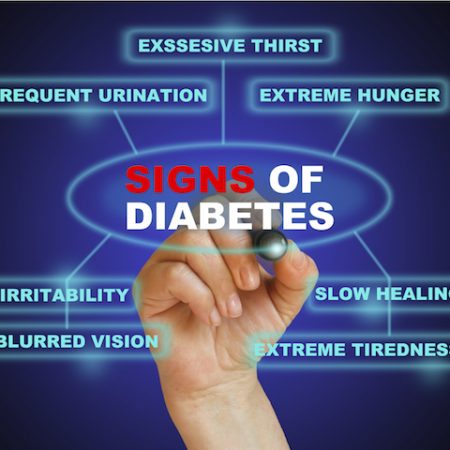
Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Increased hunger and thirst
- Increased urination
- Feeling fatigued
- Weight loss
- Blurry vision
- Slow healing sores
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
TYPE 1 DIABETES – 10-15% CASES
In Type 1 diabetes the pancreas stops making insulin. Without any insulin whatsoever the body must find a way to survive. It begins to burn the body’s own fats instead. When this occurs there is an accumulation of dangerous substances in the blood called Ketoacidosis. Type 1 diabetes means taking insulin injections daily to survive.
TYPE 2 DIABETES – 85-90%
Type 2 diabetes is most common and is diagnosed in old age. Due to the pancreas not making enough insulin= high blood glucose. Type 2 is often found in individuals carrying excessive weight. They typically eat foods lacking in nutrients and have no physical activity or minimal. Genetic predisposition to diabetes is also another factor that a positive diagnosis may indicate.
Other types of diabetes include Prediabetes, Gestational Diabetes and Secondary.
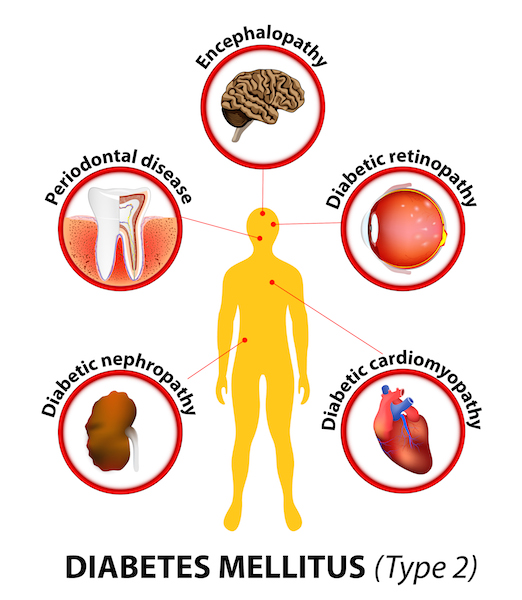
Causes of Diabetes
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
When the body’s own immune system has attacked and destroyed the cells where insulin is made., this is type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes has genetic risk factors as well as environmental factors concerning its cause. A theory debated is whether type 1 diabetes may occur after having a specific virus. To live with type 1 diabetes, the patient must take insulin every day. As there is no known cure., management of the disease is made possible by keeping blood glucose (sugar) levels within normal range.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
More common than Type 1 diabetes, in Type 2 diabetes the body does not make enough of its own insulin or cannot make use of its insulin as effectively as it should. The risk increases with age. Genetics and lifestyle play a role in the risk one has toward developing Diabetes. Type 2 diabetes has been linked to obesity, genetic risk factors, and inactivity. Racial and ethnic groups such as the Hispanics / Latino, African Americans, and Pacific Islanders are at a greater risk for this type of diabetes.
There is no known way to cure type 2 diabetes, but it can be controlled by keeping the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood within a normal range.
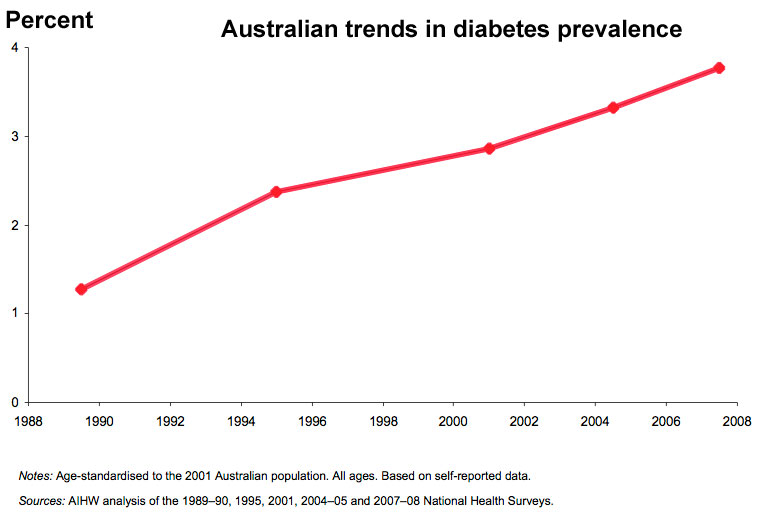
Diabetes – Emerging in epidemic proportions
Chronic health condition – Type 1, Type 2, Gestational and Other Diabetes
Clinical Studies / References: