Treatment Objectives
Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
Parkinson's Disease Treatment
In today’s world prevention is just as important as in finding a cure. As there has been no known “cure” for Parkinson’s to date, those suffering from Parkinson’s Disease will ordinarily require medications to minimise symptoms, coupled with the use of complimentary therapies or surgery. Parkinson’s disease patients may also find alternative and holistic therapies to be helpful.
Parkinson’s Disease drug treatments are designed to control the symptoms. They do this by increasing the levels of dopamine that reach the brain. There are other mechanisms of action such as in the stimulation of areas in the brain where dopamine is working. Patient response to prescribed drugs does vary dependent on the person, thus one medication may not work for all Parkinson’s patients.
Medications for the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
Carbidopa/Levodopa therapy – Levodopa increases dopamine levels in the brain, this in turn relieves the mobility issues related to Parkinson’s Disease
Dopamine Agonists – increase the dopamine levels in the brain but are reported not to be as effective as Levodopa for mobility issues but they have been reported to slow disease progression.
Anticholinergics – less commonly prescribed, these block the action of acetylcholine which is a chemical messenger that assists with sending messages from ones nerves to their muscles.
MAO-B Inhibitors – usually used as an add-on medication. MAO-B inhibitors work by blocking the breakdown of the brain’s dopamine. This makes more dopamine available which can then reduce Parkinson’s disease motor and mobility symptoms.
Other Parkinson’s Disease Treatments
- Cam Therapy
- Accupuncture
- Cognitive Therapy
- Treatment of Mood Disorder
- Treatment of Pain
- Massage Therapies
- Deep Brain Stimulation
Medicinal Cannabis Treatment for Parkinson’s Disease
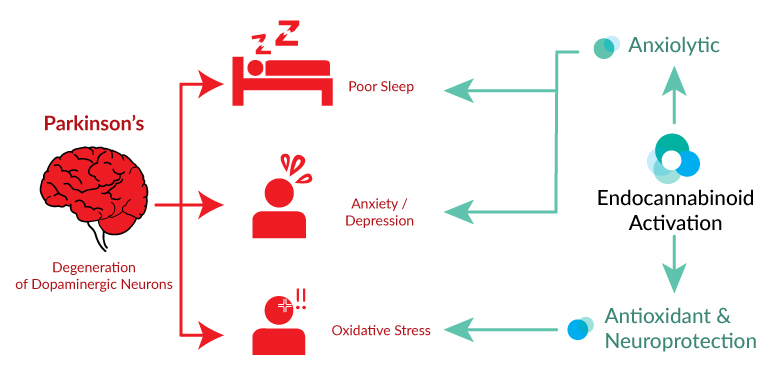
Clinical studies have deduced an improvement in motor symptoms related with Parkinson’s disease due to CBD oil:
|
|
Parkinson’s Disease – Statistics in Australia
- 4 in every 1000 people in Australia
- 1 in every 100 people over 60 years old
- 80,000 people living in Australia have Parkinson’s Disease
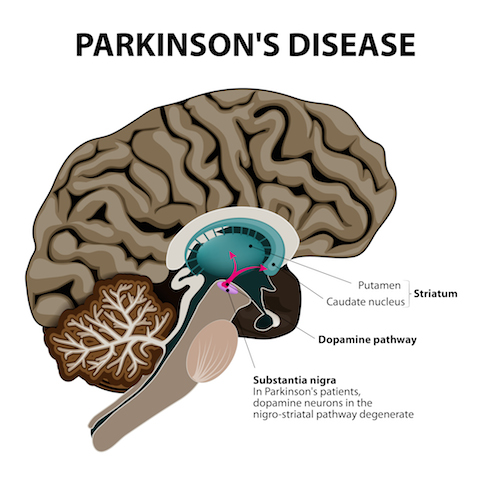
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s Disease is a disease of the nervous system that progressively worsens with time. Those suffering from Parkinsons will experience tremor, the tightening of muscles, which is referred to as “rigidity”. Parkinson’s disease is more prevalent with age. The onset occurs around middle age but is said to increase greatly among the elderly. The cause of Parkinson’s disease is associated with the degeneration of the nerve cells (neurons) located in the basal ganglia of the brain. This then causes a deficiency of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is the chemical messenger responsible for most controlled movements.
Causes of Parkinson’s Disease
- Pesticides
- Toxins
- Exposure to chemicals
- Genetic
- Head Trauma
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
- Tremors (Shakes)
- Slow Movement
- Rigidity (Tight, stiffening of muscles)
- Sleep Disturbances
- Lethargy (Overly tired)
- Stooped posture
- Small handwritin
Other complications from Parkinson's Disease include:
- Aspiration
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Pulmonary Embolism
Falls are what makes this disease dangerous for the elderly. There are large risks for a Parkinson’s patient who is in the 4th and 5th Stages of the disease. This is a time when the patient will be extremely prone to fractures and broken bones.
Clinical Studies / References: