Treatment Objectives
Arthritis
Arthritis
The pain associated with arthritis is a true menace and unfortunately only gets worse for wear, particularly in the colder months. Patients have a number of options for arthritis treatment which are in the form of medication. These may alleviate symptoms, though side effects must be noted for suitability.
Medications for the treatment of Arthritis
- Analgesics – to relieve pain
- Biologics – response modifiers
- Immunosuppressants
- NSAIDs
- Corticosteroids – glucocorticoids mimic hormone cortisol
- DMARDS – (Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs) – slows or stops inflammation
- Opiods
- NSAIDs – relieves pain and inflammation
- Topical Analgesics
- Teriparatide (Forteo) – may help heal jaw bone loss caused by periodontal disease
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections
Typical side effects of Arthritis Medication
- nausea and vomiting
- abnormal liver function / liver damage
- mouth sores
- rash
- diarrhea
- hair loss
- may effect vision
- sun sensitivity (risk of skin cancer)
- kidney damage
- high blood pressure
- risk of lymphoma
Alternative therapies for Arthritis:
- Acupuncture
- Weight management
- Exercise
- Magnetic therapy
- Physiotherapy
- Hydrotherapy
- Hot and cold treatments
- Dietary modifications – increase in fatty acids, and herbal supplements
Medicinal Cannabis Treatment for Arthritis
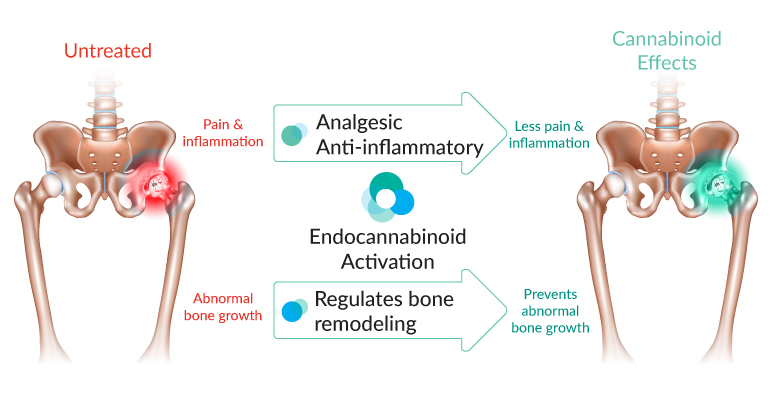
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a modulatory system in the body, ensuring homeostasis in many of the bodies natural functions. The ECS has been shown to mediate both the inflammatory cascade as well as the bone remodelling cycle.
Bone remodelling is the essential process by which bone is remodelled and repaired. Various hormones, peptides and cytokines coordinate this regularly occurring process. The key cells involved in bone remodelling are Osteoclasts, osteoblasts and osteocytes. These cells all also express CB2 receptors suggesting the ECS plays an important modulatory role.
The ECS has been implicated in maintaining homoeostasis in some ways, specifically:
- Cannabinoids are also thought to influence osteoclast-osteoblast binding
- Osteoblast cultures from CB1 knockout mice express less RANKL (cytokines for osteoclast formation) reducing the potential for bone resorption.
- CB2 knockout mice show accelerated age-related osteoporosis. Similarly activation of CB2 receptors increased bone formation markers
- Activation of the endocannabinoid system has been demonstrated to modulate the inflammation by acting at some critical junctions within the inflammatory cascade.
ECS is postulated to modulate macrophage and mast cell activation pro-inflammatory cytokines T cell proliferation and apoptosis.
The inflammatory reaction inside the joint causes a release of noxious stimuli and inflammatory mediators, leading to pain and loss of mobility.
Activation of the ECS has been shown to reduce pain signals in both the peripheral and central nervous system. The precise mechanism of action is thought to be through the excitation of the descending antinociceptive pathway as well as inhibition of painful inflammatory mediators.
The endocannabinoid system shows great promise to treat both the underlying cause of osteoarthritis as well as provide symptomatic relief from pain and inflammation.
Medical cannabis contains potent anti-inflammatory compounds as well as natural analgesics suitable in actually treating the joint pain and inflammation from arthritis.
In a 2005 study, THC and CBD (cannabidiol) were found to produce notable improvements in pain, quality of sleep, and to reduce disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Both these compounds are among the cannabinoids naturally occurring in medical cannabis. In 2000, researchers found that CBD (cannabidiol) “effectively blocked progression of arthritis” in animal trials.
Although both these studies involve cannabinoids administered as drugs isolated from the cannabis plant, medicinal use of cannabis by vaporizing, or eating, may be a better delivery method for the same potent analgesics and anti-inflammatories.
Statistics: Population Diagnosed with Arthritis in Australia
In 2011-12, 14.8% of Australians which works out to be around 3.3 million people had been diagnosed with arthritis. There was higher prevalence amongst women than men (17.7% compared with 11.8%).
Of persons with arthritis, more than half (55.9%) had osteoarthritis, 13.6% had rheumatoid arthritis, and 37.3% had a type of arthritis that was unspecified.
The prevalence of arthritis increased with age, from less than 1% of people aged under 25 years to 52.1% of people aged 75 years and over. Women aged 45 years and over were considerably more likely to have arthritis than men. In particular, at ages 75 years and over, 59.9% of women had arthritis compared with 42.3% of men.

What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is not one single disease. It is a term that covers a large number of medical conditions related to the musculoskeletal system and the joints where two or more bones meet. Arthritis is indicated by pain and stiffness caused by inflammation within the joint cartilage and surrounding structures. Arthritis can interfere with ones mobility. Patient’s experience pain and weakness in the joints, making them unstable on foot, this with the simplest of daily tasks. Though there are over 100 forms of arthritis, there are 3 that are of great significance accounting for 95% of cases diagnosed in Australia:
- Osteoarthritis is a characterised by progressive cartilage degradation, leading to inflammation, pain, abnormal bone growth and loss of mobility. Osteoarthritis is commonly associated with the reduction in joint cartilage, and compromised bone integrity.
- Rheumatoid arthritis – an autoimmune condition that also causes severe pain.
- Gout – caused by a build-up of a waste such as uric acid, in the bloodstream. As it settles in the joints it causes inflammation, pain and swelling.
Causes of Arthritis
-
Your genetic makeup
-
A job that requires you to exert a lot of physical action – particularly one with repetitive movements
-
An injury from the past
-
Some infections or allergic reactions may cause short-term arthritis. When it is caused by an infection it is known as “reactive arthritis”
-
For a number of people certain foods can activate symptoms of arthritis symptoms, or make existing ones worsen
-
Obesity, which places extra strain on joints
-
Arthritis may also be caused by autoimmune disease
Symptoms of Arthritis
- pain
- swelling in a joint
- redness and a feeling of warmth in a joint
- stiffness or difficulty moving a joint
- general symptoms such as fatigue and feeling unwell
Clinical Studies / References: