Treatment Objectives
Osteoporosis Treatment
Osteoporosis Treatment
Osteoporosis is largely preventable. Eating a well- balanced diet, consuming calcium rich foods and avoiding toxins from smoke, alcohol and caffeine greatly reduce ones chances of developing this disease.
Medication for the treatment of Osteoporosis
Bisphosphonates are typically prescribed for osteoporosis. They work by decreasing the activity of bone-dissolving cells. Bisphosphonates slow down the process of bone breakdown that occurs as you age.
Alendronate (Fosamax)
Risedronate (Actonel)
Ibandronate (Boniva)
Zoledronic acid (Reclast)
Typical side effects from Osteoporosis Medication:
- flu symptoms
- fever
- muscular pain
- joint pain
- headache
Alternative treatments for Osteoporosis
- Vitamin D
- Green Tea
- Regular Exercise
- Calcium and Magnesium
How do most osteoporosis medications work?
With the exception of teriparatide, osteoporosis drugs slow bone breakdown. Healthy bones continuously break down and rebuild. As you age and, for women, especially after menopause, bones break down faster. Because bone rebuilding cannot keep pace, bones deteriorate and become weaker.
Osteoporosis medications put a brake on the process. These drugs maintain bone density and decrease the risk of breaking a bone as a result of osteoporosis
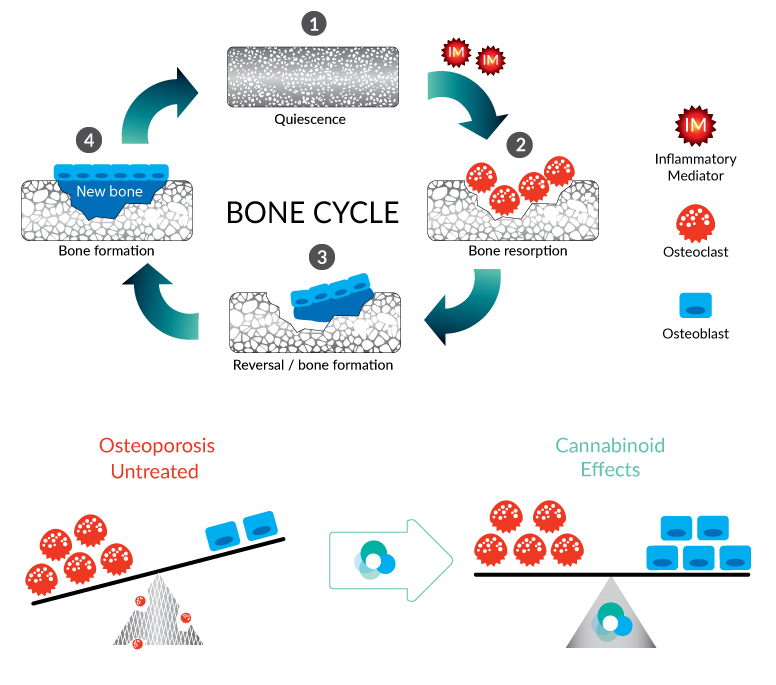
Medical cannabis treatment for osteoporosis.
The Endocannabinoid System and Osteoporosis
- CB1, CB2, TRPV1 and GPR55 receptors are known to be found in the skeleton
- CB1 receptors are found on nerve fibres intervening bone as well as cells in the bone marrow
- CB1 receptors are also found on osteoblasts, osteoclasts and bone marrow derived adipocytes
- Osteoclasts, osteoblasts and osteocytes also express CB2 receptors at significantly higher levels than those reported for CB1
In 2009, there was a group of researchers from the University of Edinburgh (UK) who published a study in the journal Cell Metabolism. Their study suggests that activation of the CB1 receptor is primarily responsible for the benefits of cannabis in treating osteoporosis.
The University of Edinburgh research team investigated whether the endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a role in osteoporosis as a condition. The team used two groups of mice in their study, one of which included rodents who had no CB1 receptors. The findings were rather interesting, in that the mice who were absent of CB1 receptors were the ones suffering from age-related osteoporosis, despite an increase in bone mass.
Lead author in the study, Ayman Idris, Ph. D explains: “the CB1 receptor is therefore unique in that it regulates peak bone mass through an effect on osteoclast activity, but protects against age-related bone loss by regulating adipocyte and osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells.”
Statistics Osteoporosis in Australia
Osteoporosis and low bone density (osteopenia) are common in Australia. Minimal trauma fractures resulting from osteoporosis are also common. Generally, osteoporosis is under-diagnosed and the prevalence of the disease is expected to increase over the next decade.
4.74 million Australians over 50 have osteoporosis or poor bone health.
There is one fracture every 3.6 minutes in Australia (2013). By 2022, there will be one split every 2.9 minutes.
144,000 fractures occurred due to osteoporosis or osteopenia in 2013.
Over the next 10 years, the total cost of osteoporosis and associated fractures is estimated to be $33.6 billion.
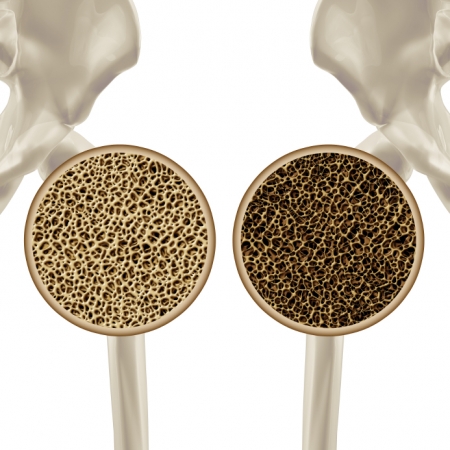
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis – literally by definition means ‘porous bones’. Porous bones are weak bones. With a reduced bone density they are easy to fracture and often may deform the physical structure of the body, such as that in spine deformities.
Osteoporosis is one of the most common metabolic bone diseases in Australia.
Diagnosis and Early Signs of Osteoporosis
Osteopenia refers to early signs of bone loss which has the potential to turn into osteoporosis. Bone health is measured by bone density. Our peak bone mass is reached by the age of 30. This is where they reach their maximum strength and density. After which, we experience the decline. After we hit 30 (approximately) our bodies begin to reabsorb bone faster than new bone can be developed. Also with age, our bodies reabsorb calcium and other minerals from our bones. The reabsorption makes our bones weak and oftentimes leads to osteopenia and osteoporosis. The vulnerability within our bones becomes clear with each new injury and fracture.
Bone Density Scan – DXA Scan
The most reliable way to diagnose osteoporosis is to have your bone density measured. This is done utilising a dual-energy absorptiometry scan which is referred to as a DXA scan. A DXA scan is a brief and painless scan which accurately measures bone mineral density. (BMD)
Bone mineral density(BMD) is related to bone strength. A bone density scan, or test, is not the same as a bone scan. A bone scan is used to find tumours, cancer, infections of the bone and fractures. It has been said that almost 80% of a persons bone density is determined by genetics. The other 20% is determined by a person’s lifestyle.
Prevention of Osteoporosis
We all like to keep active. The following list may ward away osteoporosis. Particularly if there is a family history., partaking in preventative strategies will minimise your chances of developing this debilitating condition.
- Eat High in Calcium
- Absorb Plenty Vitamin D
- Avoid exposure to pollutants such as cigarette smoke
- Limit the consumption of alcohol and caffeine
- Weight-bearing and strength training exercises and activities highly recommended
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Back pain, caused by a fractured or collapsed vertebra.
Loss of height over time
Frequent bone fractures
Stooping posture
Who is at risk for developing Osteoporosis?
- Middle Aged thru Seniors
- Family History of Osteoporosis
- Ethnicity – Asian or Caucasian
- Long term use of Corticosteroids & Anticonvulsants
- Low body weight
- Low hormone levels
- Malnutrition
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking
- Low Levels of Vitamin D
Clinical Studies / References: