Treatment Objectives
COPD Treatment
COPD Treatment
COPD – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Treatment
When there has been damage to the lungs and airways the body develops certain groups of conditions which make it hard for a patient to breathe normally. COPD treatment is not a cure, but it does improve the quality of life for that of the patient by opening the airways and reducing inflammation. Acquiring the knowledge of what dietary choices best help COPD, and following the direction of medical professionals, COPD symptoms can be minimised.
Medications for the treatment of COPD
Short-Acting Bronchodilators
These kinds of medications help open the airways enabling the patient to breath easier. Short- Acting usually means this medicine has been prescribed for quick relief or in an emergency situation. This medication comes as an inhaler or it comes as a liquid that is then added to a nebuliser for inhalation.
Typical side effects may include:
- Tremors
- Dry Mouth
- Blurred Vision
- Cough
- Fast heart beat
Corticosteroids
This type of medication reduces inflammation in the body. With less inflammation more air flow can pass through the lungs, making it easier to breathe. Corticosteroids and bronchodilators are typically prescribed together for the best relief to the patient.
Methylxanthines
Some doctors will prescribe theophylline, when the first line of defence is not doing such a great job for the patient (corticosteroids and bronchodilators). Relaxing the muscles in the airway, this medicine is ordinarily taken with a bronchodilator. Theophylline comes as a pill or a liquid. It is taken on a daily basis and is an effective COPD treatment that helps patients breathe easier.
Typical side effects may include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Tremors
- Insomnia
Long-Acting Bronchodilators
Long-acting bronchodilators are medications used to treat COPD for a longer period. Taken one or two times daily, this medication comes as an inhaler or a nebuliser.
tiotropium (Spiriva)
salmeterol (Serevent)
indacaterol (Arcapta)
aclidinium (Tudorza)
formoterol (Foradil, Perforomist)
arformoterol (Brovana)
Typical side effects may include:
- Runny nose
- Dizziness
- Tremors
- Dry Mouth
- Scratchy throat
- Rash
- Blurred vision
- Fast heart rate
LTOT -Long term oxygen therapy is a prescribed therapy for those suffering from COPD that gives supplemental oxygen for 15 hours per day or more if required. For those patients with persistently low levels of oxygen in the blood, particularly those suffering from a chronic lung disease. (advanced COPD) This selective LTOT has been shown to increase the quality of life as well as lengthen the life span for those with advanced COPD (Lung Foundation Australia 2012).
Pulmonary rehabilitation
This care is a combination that includes:
- Education – Nutritional guidance, medication use guidelines
- Exercise Training – maximising skeletal muscle, improved technique in breathing, optimisation of cardiovascular fitness and maintenance of a fitness regime.
- Psychosocial Support – support groups and organisations can offer emotional, social support and coping strategies.
Helping sufferers of COPD to maintain optimal independence and functionality. (Lung Foundation Australia 2008).
Medical Cannabis Treatment for COPD
There is no known cure for COPD at this stage in time. Symptoms can be relieved in a number of ways including oxygen therapy, anticholinergics ( these help relax muscles ) and through pulmonary rehab. Pulmonary rehab includes exercise, education and nutritional support.
How Cannabinoids may help COPD
- Cannabinoids relieve inflammation
- Cannabinoids are anti-microbial
- Cannabinoids support / modulate the immune system and its response to infection and disease
- Cannabinoids are expectorants
- Cannabinoids are analgesic (pain relief)
- Cannabinoid medicine has little to no side effects
In COPD, air flow is restrictive due to:
- The airways + air sacs have a lack of elasticity
- Air sac destruction and inflammation
- Increased mucus and clogged airways
- 1 in every 20 people in Australia aged 55+ has some form of COPD
- 310,700 people have COPD in Australia
- 5th leading cause of death

What is COPD?
COPD – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Progressive disease (worsens over time)
- Chronic Bronchitis – Long term cough with mucous
- Emphysema is the result of destruction of the lungs over the course of ones life
Causes of COPD
Smoking cigarettes has been proven to deliver a whole array of chemicals that should not be inhaled into the lungs. In order for COPD to improve, jt is imperative patient’s refrain from smoking and immediately. The damage from having a smoking habit or being in close proximity (second hand) with cigarette smoke is one of the main causes for COPD. Exposure to pollutants, fumes, even harsh cleaners have the ability over time to cause damage to your lungs. Asthma sufferers also have a strong tendency to develop COPD.
Symptoms of COPD
- A persistant cough that is worsened within the early hours of the morning.
- Excess mucous – someone suffering COPD will produce 3x the mucous if exposed to irritants
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Fatigue and extreme tiredness
- Frequent flare ups
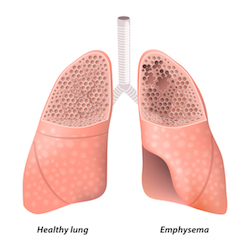
What is Emphysema?
- Emphysema is among a group of diseases called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD.
- Emphysema is referred to as an obstructive lung disease due to the destruction that is evident within the lung tissue.
- Emphysema is a long-term, progressive disease which causes a patient to be short of breath.
- Emphysema is classified as primary or secondary emphysema.
Emphysema is commonly classified by location into panacinary (panacinar) and centroacinary(centriacinar).
Panacinar emphysema: The entire respiratory acinus is expanded. This includes everything from the respiratory bronchiole to alveoli. Mostly this will occur within the lower lobes, basal segments, and anterior margins of lungs.
Centriacinar emphysema: The respiratory bronchiole becomes expanded. The distal acinus or alveoli don’t change. Occurs in the upper lobes.
Clinical Studies / References: